Specification designing in plastics
The product that is chosen to be worked out is the housing of the wheel. It was chosen because it is a key component in the Storsjön and needs to be able to withstand the whole weight of the closet. What needs to be reconsidered is that the housing will be made for IKEA so it needs to be as cheap as possible, environment friendly and as simple as possible.
Calculations
Calculation of the requirements of the material. To optimize the product there need to be precise calculations for the housing.
The iterations are:
Dimensions: ( 70*90*50)mm (length, width, height)
Dimension of the hole = 7mm
Thickness of the material 2mm’
Mass of the Storsjön = 100kg
Force exerted = 100*9,81= 981N
First the forces that are going to be exerted on the housing will be explained.
First the shear forces are calculated, this can be done with the formula:
Tau=F/A With Tau as the shearstress , F the load, and A the surface.
Tau=F/A
981/(2*(2*70)) = 3,5 MPa
Now the tension of the pin joint are calculated.
The formula of the tension is
sigma = F/A
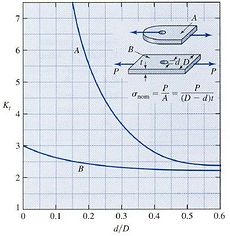
But because the force is exerted on an round smaller surface there will be stress concentration factors involved. Because of this factor the wall thickness will be doubled around the pin joint. These can be read out of figure…. the concentration factor is dependent of the with of the housing and the radius of the hole.
d/D=7/70=0.1
This factor is too small for the graph so the maximum concentration factor will be taken. This is 7.5.
sigma = (F/A) * Kt = (981/(pi*7*4)) * 7.5 = 42MPa
Translation of the requirements
Function:
The wheel housing transfers the force exerted by the Storsjön on the wheel. It is also protection for the wheel so nothing can come in contact with it.
Design:
When a product is injection moulded the design should be.
To optimize the stiffness of the structure there will be ribs attached to the flanshes.
Constraints that must be met by the material are:
-
Cheap material
-
Strong material
-
It needs to be injection moulded
-
The material needs to withstand temperatures between -10 and 80 °C
-
The material may deform 1 mm because of the pressure.
-
The material may deform 1 mm because of the temperature difference.
-
The material needs to be water resistant.
The objective:
The objectives are to optimize the design so the walls can be made as thin as possible and still bear with the applied force. It is also important that the cheapest material possible will be selected so the costs of Ikea will be reduced.
Free variables:
The material needs to be as environment friendly as possible so the CO2 footprint needs to be as small as possible.
Material selection
Narrowing the selection.
To narrow down the selection of usable materials the following parameters are used in CES Edupack.
* Tensile strength - Min 50 MPa
* Max. service temperature - 80*C
* Minimal service temperature - -10*C
* Injection molding - excellent
* Maximal price - €3,-
1. Young's modulus (GPa)
2. Yield stregth (MPa)
3. Service temperature (*C)
4. Costs (€)
5. CO2 footprint (kg/kg)
Choosing the material
The materials will be rated on their performance the best material gets thee points and the least sufficient material will only get one point. The rating of the material will be multiplied with the Weighing factor and be counted. The material that receives the most points is the material that is going to be used.
Conclusion
PET is by far the best material for the housing of the wheel so this is the material that is going to be used as the material for the wheel housing.